Hey there! Are you a music enthusiast looking to explore the world of jazz? Well, you’re in for a treat because today, I want to dive into the captivating realm of the “Misty” lead sheet. As a seasoned musician myself, I can assure you that this iconic jazz standard has captivated audiences for decades with its dreamy melodies and lush harmonies. In this article, I’ll break down the essence of the “Misty” lead sheet, exploring its origins, structure, and why it remains a beloved tune among musicians and listeners alike. So, grab your instrument or sit back and relax, because we’re about to embark on a musical journey like no other!
If you’ve ever found yourself lost in the enchanting melodies of jazz music, chances are you’ve come across the timeless classic, “Misty.” This beloved tune, composed by the legendary Erroll Garner, has become an integral part of the jazz repertoire. In this article, I want to take you behind the scenes of the “Misty” lead sheet, unraveling its secrets and shedding light on why it continues to resonate with musicians and audiences worldwide. From its hauntingly beautiful melodies to its rich harmonic language, we’ll explore the essence of this iconic jazz standard and discover what makes it so special. So, get ready to immerse yourself in the world of “Misty” as we uncover the magic behind the notes.
Misty Lead Sheet
As a musician, exploring the origins of a beloved jazz standard like the “Misty” lead sheet is like diving into a treasure trove of musical history. This iconic composition was written by Erroll Garner, a talented pianist and composer, in 1954. “Misty” has since become a staple in the jazz repertoire, loved by both musicians and audiences worldwide.
Erroll Garner’s inspiration for “Misty” came from a simple chord progression. The first four bars of the song are built on a chromatic descending line in the right hand, accompanied by colorful chords in the left hand. This mesmerizing harmonization gives “Misty” its unique and captivating quality.
Interestingly, Erroll Garner originally composed “Misty” as an instrumental piece, without any lyrics. However, Johnny Burke, a renowned lyricist, later added heartwarming words to the melody, transforming it into an even more enchanting song. This collaboration between Garner and Burke elevated “Misty” to a whole new level of popularity.
The beauty of “Misty” lies in its ability to evoke deep emotions with its captivating melody and harmonic progression. The song’s nostalgic and dreamy atmosphere has made it a timeless classic, capable of captivating listeners of all ages. Whether you’re sitting in a dimly lit jazz club or enjoying a cozy evening at home, the enchanting music of “Misty” transports you to a world of warm emotions and serene tranquility.
Today, “Misty” remains one of the most covered jazz standards, performed by countless musicians across various genres. Its universal appeal stems from its ability to transcend boundaries and connect with people on a profound level. From jazz legends to contemporary artists, the allure of “Misty” continues to attract performers who seek to convey their own interpretation of this iconic composition.

Structure Of The “Misty” Lead Sheet
When examining the structure of the “Misty” lead sheet, we can unravel the genius behind this timeless jazz standard. The lead sheet provides a framework for musicians to interpret the composition while leaving room for improvisation. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements that define the structure of the “Misty” lead sheet:
- Form: The lead sheet follows a typical AABA song form, consisting of four sections: A, A, B, A.
- Section A: The opening section introduces the main melody and establishes the harmonic progression of the song. This section is repeated twice.
- Section B: Known as the bridge or contrast, the B section provides a refreshing change in tonality and serves as a departure from the A section.
- Section A (variation): The final A section returns, but with slight variations or embellishments, adding a sense of familiarity while keeping the performance fresh.
- Chords: The “Misty” lead sheet includes the chord symbols that accompany the melody, enabling musicians to comp or improvise harmonically. Some of the recurring chords include:
- Major seventh chords: These lush and rich chords characterize the romantic essence of “Misty.” Examples include Cmaj7, Fmaj7, Gmaj7, and Bbmaj7.
- Dominant seventh chords: These chords add tension and create harmonic movement, enhancing the emotional impact of the composition. Common examples include Bb7, Eb7, and Ab7.
- Melody: The lead sheet displays the iconic melody of “Misty,” capturing its captivating charm. The melody is written in standard musical notation, allowing musicians to interpret and imbue it with their own expression and style.
- Lyrics: Although primarily an instrumental piece, “Misty” does have heartwarming lyrics written by Johnny Burke. While the lead sheet focuses on the melody and chords, the lyrics convey the romantic sentiments and can be sung if desired.
By understanding the structure of the “Misty” lead sheet, musicians can appreciate the compositional brilliance of Erroll Garner and Johnny Burke. The flexibility it offers allows for endless interpretations, ensuring that “Misty” remains a beloved and enduring jazz standard.

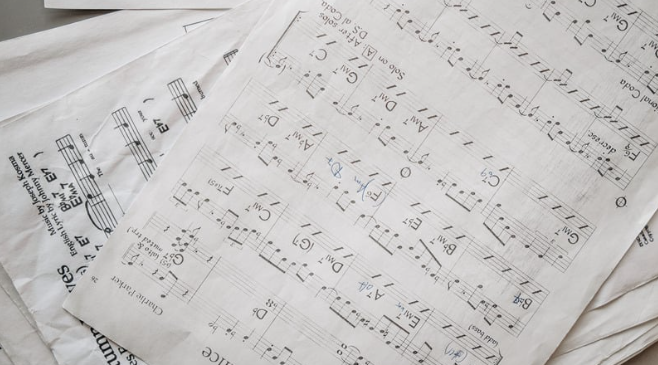
More Stories
Safe Online Entertainment for Residents of Voorne-Putten
Strategies To Boost Your Website’s Visibility Using High-authority Platforms
Breaking Down the Appeal of Non-GamStop Betting Sites